Selaginellaceae polyphenols
Selaginella pulvinata and Selaginella tamariscia belong to the genus selaginella (Selaginellaceae) and were used in traditional folklore medicine. In recent years, various polyphenols with intriguing chemical structures were isolated from these species, including selaginellins, selaginpulvilins, selagibenzophenones, selaphenins, and selaginones. The unusual structural motifs and the potential for the application in medicinal chemistry are the main motivations for our research in the field of Selaginellacea polyphenols research.
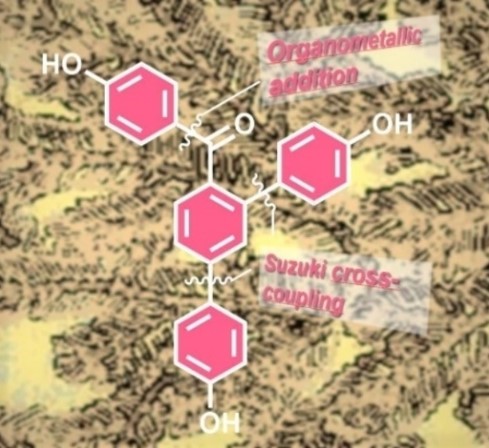
- METHODOLOGY IN TOTAL SYNTHEIS. We have carried out a formal synthesis of selginpulvilin C and D, using catalytic [2+2+2] trimerization as a key step to obtain the fluorene framework of the natural product. The regioselectivity and the course of the trimerization is governed by the nature of the used external alkyne. Read more: Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 4511-4515.
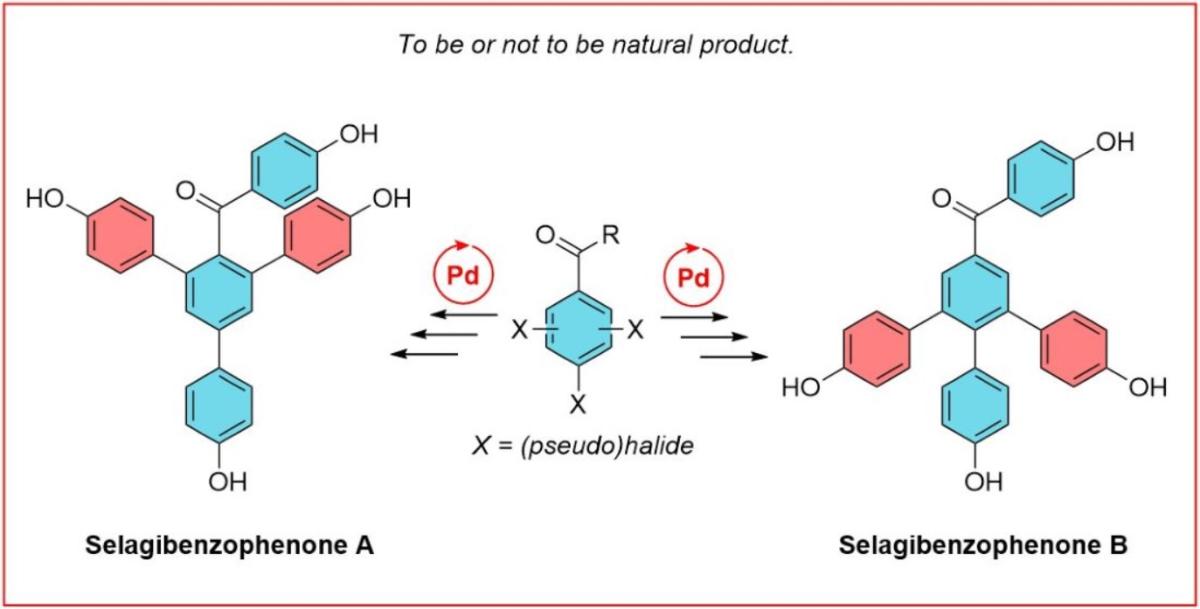
- CORRECTION OF PROPOSED STRUCTURE. We synthesized selgibenzophenoes A and selagibenzophenone B and discovered that the compound previously described as Selagibenzophenone B was incorrectly elucidated. Read more about the real structure: Catalysts 2021, 11(6)
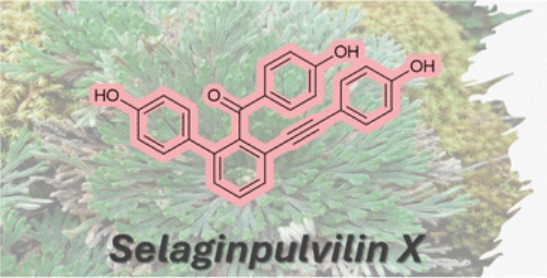
- FIRST TOTAL SYNTHESES. In line with our previous findings regarding Selagibenzophenone B structural discrepancies, we carried out the first total syntheses of Selagibenzophenone C and Selaginpulvilin X to verify their proposed structures. Read more about selgibenzophenone C (Eur. J. Org.Chem. 2022,e202200014) and selaginpulvilin X (Org. Biomol. Chem., 2024,22, 8843-8846)
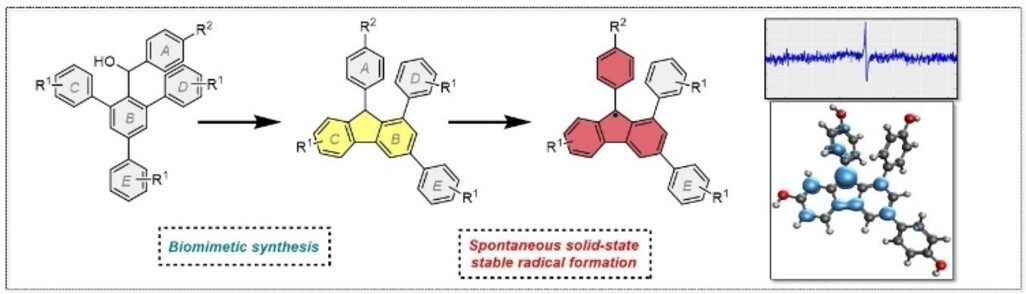
- UNUSUAL PROPERTIES. We discovered that certain unnatural, sleginpulvilin-like compounds spontaneously form solid-state, air-stable radicals. Read more: ChemPlusChem, 2024, 89, e202300410.
- SELECTIVE CYTOTOXIC ACTIVITY. We discovered, that some unnatural derivatives of selagibenzphenones are selectively cyctotoxic to prostate cancer cell lines. We shine some light on their mode of action. Read more: ACS Bio & Med Chem Au, 2024, 4, 178–189